2025/3/25大约 7 分钟
线段与AABB求交的算法
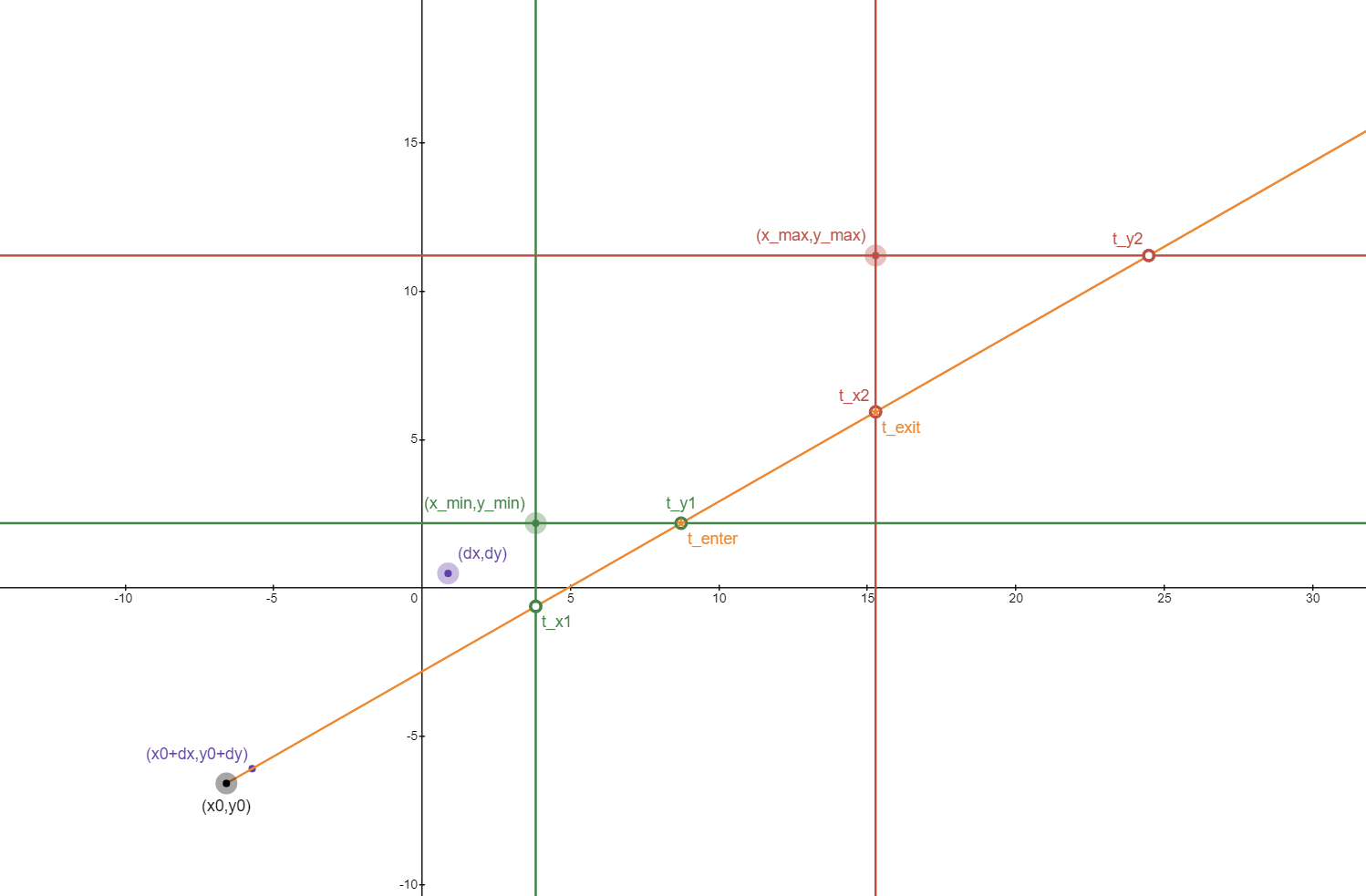
如何快速判断任意线段与任意AABB是否相交?首先想到的方法是借助射线与AABB求交的算法,获得射线进入和离开的时机,在射线与AABB相交的前提下保证进入时机在线段终点之前。
下面是搜集到的三种算法即实现,并且通过添加轴的的维度完全可以应用于三维情况。
零、 数据结构
import random
import time
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class Vec2D:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.v = np.array([x, y])
def __sub__(self, other):
return Vec2D(self.v[0] - other.v[0], self.v[1] - other.v[1])
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.v[index]
def __mul__(self, scalar):
return Vec2D(self.v[0] * scalar, self.v[1] * scalar)
def __add__(self, other):
return Vec2D(self.v[0] + other.v[0], self.v[1] + other.v[1])
def ToString(self):
return f'({self.v[0]},{self.v[1]})'
class Rect:
def __init__(self, min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y):
self.min = Vec2D(min_x, min_y)
self.max = Vec2D(max_x, max_y)
def ToString(self):
return f'{{ {self.min.ToString()},{self.max.ToString()} }}'一、 射线与AABB求交算法
假设:
- 射线起点为,方向向量为,射线方程为
- AABB包围盒表示为
算法:
- 计算射线进入各个轴的时间,取最大值作为进入AABB的时间
- 计算射线离开各个轴的时间,取最小值作为离开AABB的时间
- 判断 是否成立(先进入、后离开),成立则相交,不成立则不相交
- 如需计算交点,计算 和 即为所求
实现:
# p1决定射线起点,p1、p2共同决定射线方向
def ray_aabb(p1, p2, aabb):
d = np.linalg.norm(p2 - p1)
t_min = 0
t_max = float('inf')
for axis in range(2):
inv_d = 1.0 / d[axis] if d[axis] != 0 else float('inf')
t0 = (aabb.min[axis] - p1[axis]) * inv_d
t1 = (aabb.max[axis] - p1[axis]) * inv_d
if inv_d < 0:
t0, t1 = t1, t0
t_min = max(t_min, t0)
t_max = min(t_max, t1)
if t_min > t_max:
return False
return TrueTricks:
- 根据方向向量 在指定轴上投影 的正负决定进入和离开该轴的时间
- 某个轴上出现 的情况,必不相交
二、 线段与AABB求交算法
1. 射线法
假设:
- 线段起点为,终点为,方向 ,线段方程为
- AABB包围盒表示为
算法:
参考射线与AABB求交的算法,只是方向非单位向量,参数t的上限约束到1
- 计算线段进入各个轴的时间,取最大值作为进入AABB的时间
- 计算线段离开各个轴的时间,取最小值作为离开AABB的时间
- 判断 是否成立(先进入、后离开),成立则相交,不成立则不相交
- 如需计算交点,计算 和 即为所求
# p1决定线段起点,p2决定线段终点
def seg_aabb(p1, p2, aabb):
d = p2 - p1
t_min = 0
t_max = 1
for axis in range(2):
inv_d = 1.0 / d[axis] if d[axis] != 0 else float('inf')
t0 = (aabb.min[axis] - p1[axis]) * inv_d
t1 = (aabb.max[axis] - p1[axis]) * inv_d
if inv_d < 0:
t0, t1 = t1, t0
t_min = max(t_min, t0)
t_max = min(t_max, t1)
if t_min > t_max:
return False
return TrueTricks:
- 将线段视为有上限的射线
2. liang_barsky算法
假设:
- 线段起点为,终点为,方向 ,线段方程为
- AABB包围盒表示为
算法:
- 联立方程
- 获得满足位于AABB内的点
- 计算逐个轴中 的上下限,以x轴为例:
- 预计算不等式中的各项,以x轴为例:
- 根据预计算结果,逐轴计算实际 的上下限并判断该轴内是否可能相交,以x轴为例:
即:
- 如需计算交点,计算 和 即为所求
实现:
def liang_barsky(p1, p2, aabb):
dx = p2[0] - p1[0]
dy = p2[1] - p1[1]
p = [-dx, dx, -dy, dy]
q = [p1[0] - aabb.min[0], aabb.max[0] - p1[0], p1[1] - aabb.min[1], aabb.max[1] - p1[1]]
t0, t1 = 0.0, 1.0
for i in range(4):
if p[i] == 0: # 线段平行于矩形的某一边
if q[i] < 0: # 线段在边界之外
return False
else:
t = q[i] / p[i]
if p[i] < 0:
if t > t1:
return False # 线段完全在边界外
if t > t0:
t0 = t # 向内裁剪
else:
if t < t0:
return False # 线段完全在边界外
if t < t1:
t1 = t # 向内裁剪
return True # 线段与矩形相交Tricks:
- 中间结果预计算
- 根据被除项的正负决定是上限还是下限
3. Cohen-Sutherland算法
原理: 将整个空间用AABB四条边划分为9个区域,并对区域进行编码,根据线段两端点所在区域编码快速决定线段与AABB的关系。无法立即判断的情况下对线段进行裁剪,递归判断
实现:
- 对空间进行编码,左中右分别使用10、00、01,上中下分别使用10、00、01,并加以组合获取9个编码
| 左 | 中 | 右 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 上 | 10 10 | 10 00 | 10 01 |
| 中 | 00 10 | 00 00 | 00 01 |
| 下 | 01 10 | 01 00 | 01 01 |
获得线段两端点 , 所在区域的编码 ,
快速判断相交情况:
$ c_0 | c_1 = 0 $ , 必相交(线段全在AABB内)
$ c_0 & c_1 \neq 0 $ , 必不相交(线段两端点均在AABB某一侧)
- 其余情况需按照左右上下的顺序,求出虚交点 迭代判断
实现:
def compute_outcode(point, aabb):
# 计算点的区域编码
code = 0
for axis in range(2):
code = code << 2
if point[axis] < aabb.min[axis]:
code |= 0b01
elif point[axis] > aabb.max[axis]:
code |= 0b10
else:
code |= 0b00
return code
def cohen_sutherland_clip(p0, p1, aabb):
outcode0 = compute_outcode(p0, aabb)
outcode1 = compute_outcode(p1, aabb)
accept = False
while True:
# 如果两个端点都在裁剪窗口内,则接受该线段
if not (outcode0 | outcode1):
accept = True
break
# 如果两个端点的区域编码按位与不为零,则线段完全在裁剪窗口外
elif outcode0 & outcode1:
break
else:
# 选择在裁剪窗口外的点
outcode_out = outcode0 if outcode0 else outcode1
# 计算交点
# 需要确定是哪个边界
for axis in range(2):
# 线段与轴的下限相交
if outcode_out & (0b01 << 2 * (2 - 1 - axis)):
t = (aabb.min[axis] - p0[axis]) / (p1[axis] - p0[axis])
p = p0 + (p1 - p0) * t
break
# 线段与轴的上限相交
elif outcode_out & (0b10 << 2 * (2 - 1 - axis)):
t = (aabb.max[axis] - p0[axis]) / (p1[axis] - p0[axis])
p = p0 + (p1 - p0) * t
break
# 更新点和区域编码
if outcode_out == outcode0:
p0 = p
outcode0 = compute_outcode(p0, aabb)
else:
p1 = p
outcode1 = compute_outcode(p1, aabb)
if accept:
return True # (p0, p1)
else:
return False # None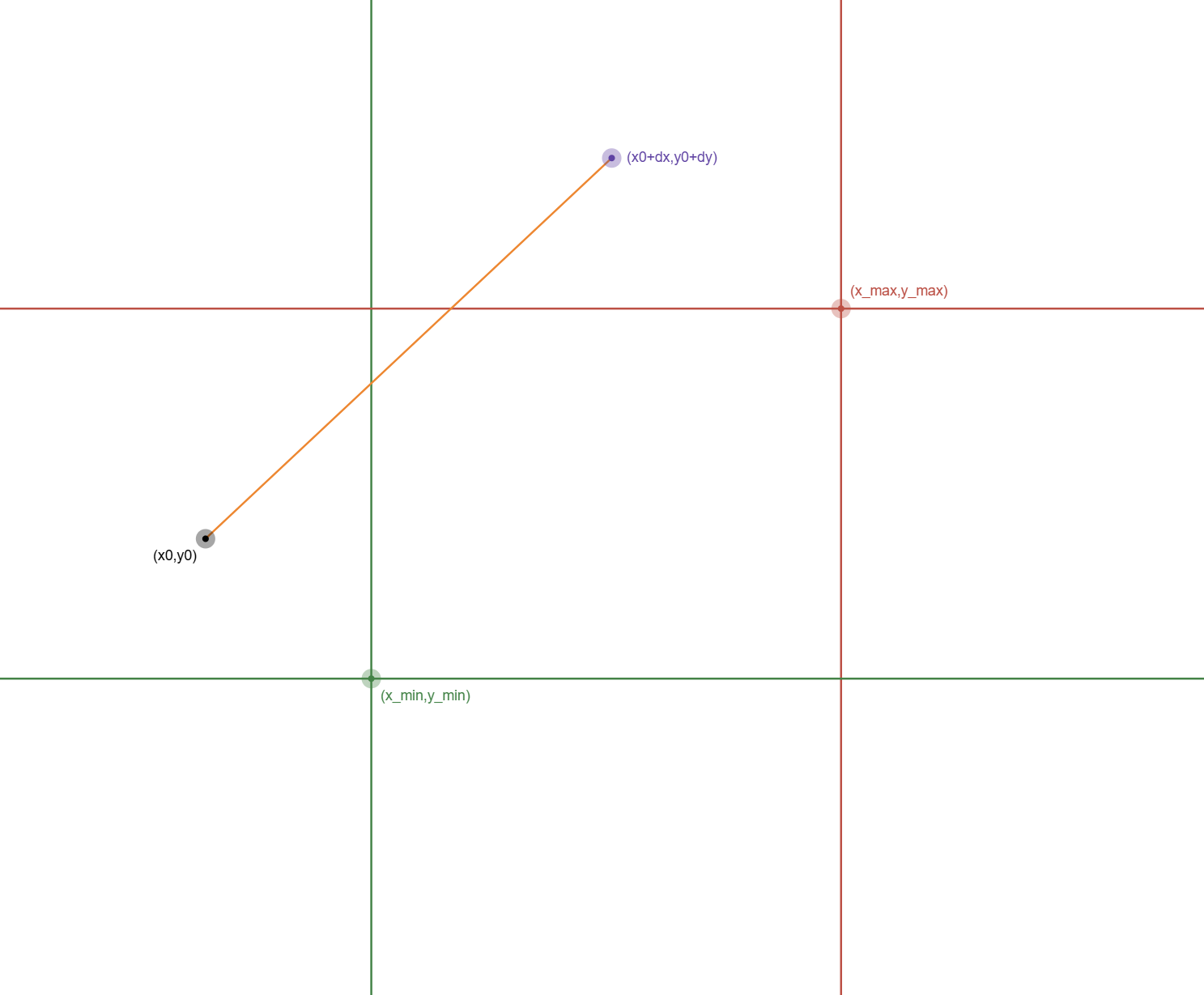
三、 测试代码
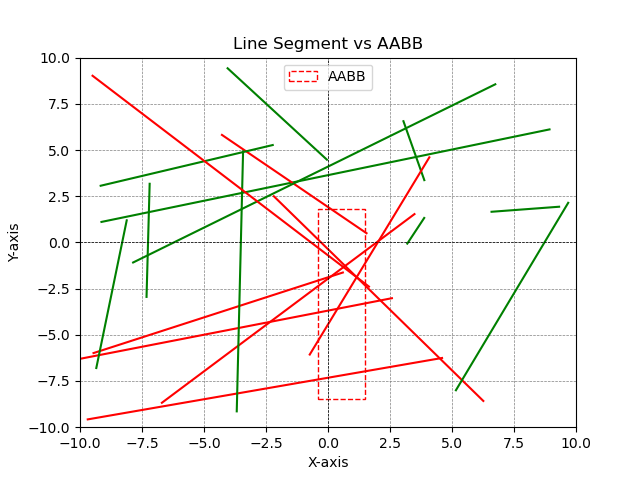
def visualize():
center = np.array([random.uniform(-10, 10), random.uniform(-10, 10)])
extend = np.array([random.uniform(0.1, 6.5), random.uniform(0.1, 6.5)])
aabb = Rect(center[0] - extend[0], center[1] - extend[1], center[0] + extend[0], center[1] + extend[1])
# aabb = Rect(2,1,3,4)
# 绘制 AABB
rectangle = plt.Rectangle((aabb.min[0], aabb.min[1]),
aabb.max[0] - aabb.min[0],
aabb.max[1] - aabb.min[1],
linewidth=1, edgecolor='r', facecolor='none', linestyle='--', label='AABB')
plt.gca().add_patch(rectangle)
for t in range(1, 20):
p1 = Vec2D(random.uniform(-10, 10), random.uniform(-10, 10))
p2 = Vec2D(random.uniform(-10, 10), random.uniform(-10, 10))
# p1 = Vec2D(-1.40,-1.79)
# p2 = Vec2D(4.54,1.39)
# 检查并显示检测结果
# is_collision = seg_aabb(p1, p2, aabb)
# is_collision = liang_barsky(p1, p2, aabb)
is_collision = cohen_sutherland_clip(p1, p2, aabb)
print(f'{p1.ToString()}->{p2.ToString()},{aabb.ToString()},{is_collision}')
if is_collision:
line_color = 'r'
else:
line_color = 'g'
# 绘制线段
plt.plot([p1[0], p2[0]], [p1[1], p2[1]], color=line_color)
# 设置坐标轴范围
plt.xlim(-10, 10)
plt.ylim(-10, 10)
plt.axhline(0, color='black', linewidth=0.5, ls='--')
plt.axvline(0, color='black', linewidth=0.5, ls='--')
plt.grid(color='gray', linestyle='--', linewidth=0.5)
plt.title('Line Segment vs AABB')
plt.xlabel('X-axis')
plt.ylabel('Y-axis')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
def test(t):
start = time.perf_counter()
for i in range(t):
p1 = Vec2D(random.uniform(-10, 10), random.uniform(-10, 10))
p2 = Vec2D(random.uniform(-10, 10), random.uniform(-10, 10))
center = np.array([random.uniform(-10, 10), random.uniform(-10, 10)])
extend = np.array([random.uniform(0.1, 6.5), random.uniform(0.1, 6.5)])
aabb = Rect(center[0] - extend[0], center[1] - extend[1], center[0] + extend[0], center[1] + extend[1])
is_collision = liang_barsky(p1, p2, aabb)
end = time.perf_counter()
runTime = end - start
print("运行时间:", runTime, "秒")
start = time.perf_counter()
for i in range(t):
p1 = Vec2D(random.uniform(-10, 10), random.uniform(-10, 10))
p2 = Vec2D(random.uniform(-10, 10), random.uniform(-10, 10))
center = np.array([random.uniform(-10, 10), random.uniform(-10, 10)])
extend = np.array([random.uniform(0.1, 6.5), random.uniform(0.1, 6.5)])
aabb = Rect(center[0] - extend[0], center[1] - extend[1], center[0] + extend[0], center[1] + extend[1])
is_collision = liang_barsky(p1, p2, aabb)
end = time.perf_counter()
runTime = end - start
print("运行时间:", runTime, "秒")
visualize()
#test(1000000)